The Pectra enhancement and other upgrades have not yet resulted in a substantial increase in Ethereum network activity, as analyzed in a new JPMorgan Ethereum report. The recent developments, which led to a spike in Ether’s price and market capitalization, attracted institutional crypto interest but failed to boost everyday user engagement, which stayed consistently low, thus casting doubts on Ethereum’s network appeal to broader audiences.
The analysis highlights a notable divergence: The vigorous involvement of institutional investors in CME futures shows a stark contrast to the weak demand from retail investors reflected in low spot Ethereum ETF inflows. The blockchain draws large financial entities because of its improved regulatory compatibility and efficiency, but fails to turn this interest into broad daily user activity, which stands as a significant obstacle to Ethereum’s growth path.
Ethereum’s Institutional Embrace vs. Stagnant On-Chain Metrics
The Pectra upgrade merged multiple Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) to boost staking efficiency and deposit/withdrawal speed while raising rewards. According to JPMorgan analysts, the combination of new features and security token standards like ERC-3643 and ERC-1400 positions ETH as a more appealing choice for institutional investors needing regulatory compliance. This reflects a strategic movement similar to BTC’s trend. The integration between ETH and real-world financial systems has been established through support from major organizations like the Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC).
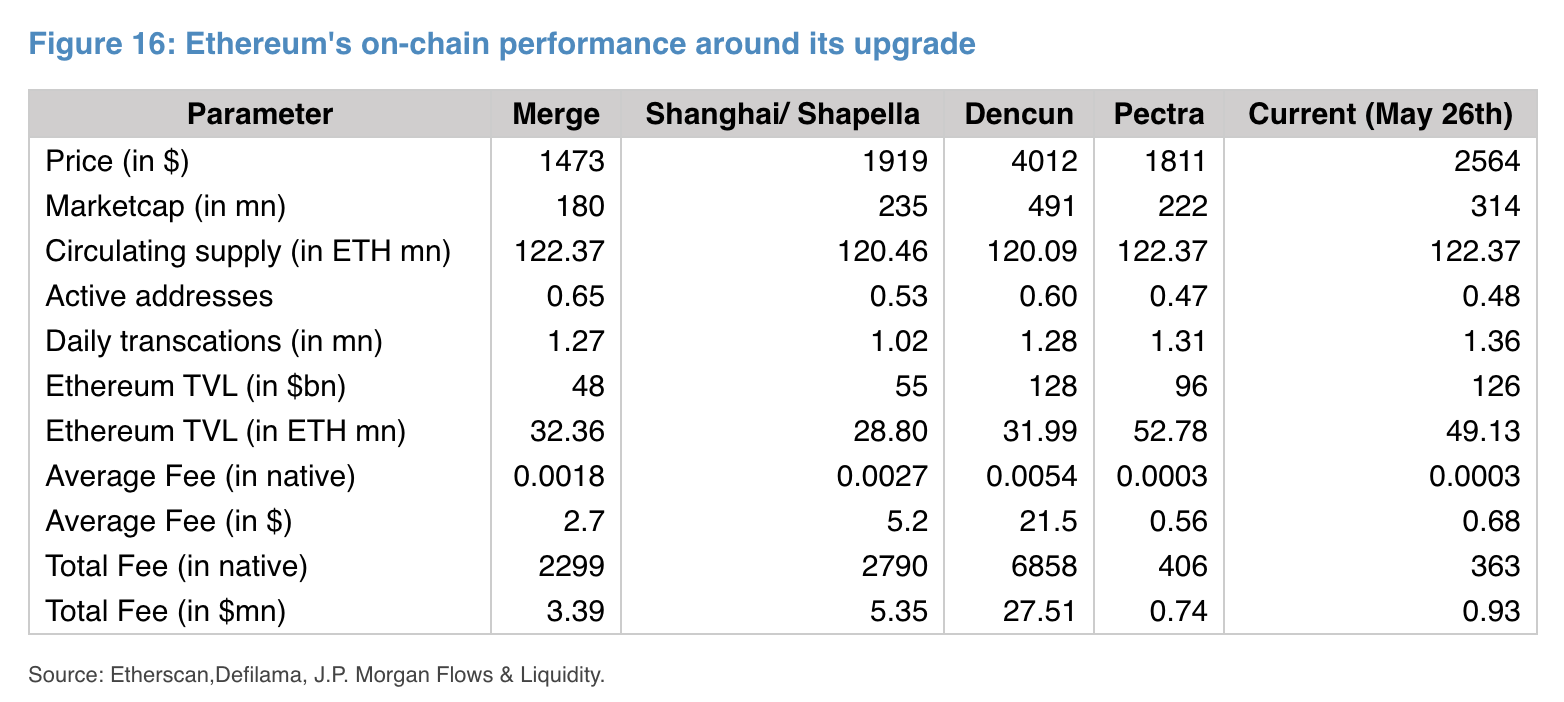
Even though Ethereum has implemented advanced enhancements and targeted institutional users, Ethereum network activity has shown little to no change. Analysts have observed that there has been no significant growth in either daily transactions or active addresses. Core usage statistics remain static, which demonstrates that enhanced institutional interest in Ethereum has failed to result in expanded user adoption or increased daily network use.
Unpacking Ethereum’s Retail Disinterest and Financial Performance
Open interest and price shifts of ETH futures on CME show JPMorgan’s institutional flow proxy, which indicates a strong rise in institutional investors taking long positions, thus proving increased institutional crypto interest. Major financial institutions are actively working to add Ethereum to their investment portfolios due to the significant rise in regulated futures trading. Institutional interest sets Ethereum apart from other platforms, which focus mainly on individual users and meme coin trends, to achieve a more advanced financial system.
The U.S. investor appetite for spot Ethereum ETFs has remained subdued compared to the strong inflows seen in spot Bitcoin ETFs after major market events. The lack of retail participation and external investor interest creates a clear divide from institutional investment activities. The disappointing performance of spot ETFs indicates widespread disinterest from average individual investors towards Ethereum despite recent upgrades and institutional developments, which results in a significant enthusiasm gap in the market.
Ethereum’s Shifting Economics: Inflation and Fee Challenges
Analysts have raised a major issue regarding Ethereum’s reduced transaction fees, which stems from decreased network activity and expanded Layer 2 network usage. The context transforms lower transaction fees into an indicator of decreased mainnet demand through diminished transaction volume. Even though total value locked (TVL) in ETH terms experienced growth from increased lending and borrowing activities, the dollar value growth has been much weaker, which signals latent instability.
The Dencun upgrade has expanded Ethereum’s circulating supply, which has resulted in a decline in its burn rate. The recent changes have triggered concerns that Ethereum is moving back towards an inflationary state, which conflicts with its “ultrasound money” concept that remains crucial for many supporters. The JPMorgan Ethereum report identifies that persistent low Ethereum network activity, combined with inflationary pressures, creates major obstacles to its economic framework and future viability.
The Future of Ethereum: Balancing Institutional Growth and User Adoption
JPMorgan’s evaluation identifies a crucial point for Ethereum, which demonstrates that while institutional engagement has been successful, it hasn’t resulted in increased fundamental Ethereum network activity. Pectra upgrades have made Ethereum more appealing to traditional financial sectors due to enhanced efficiency and compliance features, but converting this interest into widespread practical use remains a significant challenge. The disconnect between institutional excitement and stagnant network activity reveals a crucial obstacle Ethereum needs to address.
The combination of the banking giant’s subdued optimism and worries about continuous competition from other blockchains indicates that Ethereum will encounter significant challenges in establishing itself beyond institutional adoption. The network requires new strategies to boost retail participation and transaction volumes to handle inflationary pressures while increasing user engagement, which presently limits its institutional objectives.